Active Drug Delivery via the Small Intestinal Mucosa
Most drugs are taken orally whereupon being delivered from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood. In this context, the small intestinal mucosa is the major site of resorption.
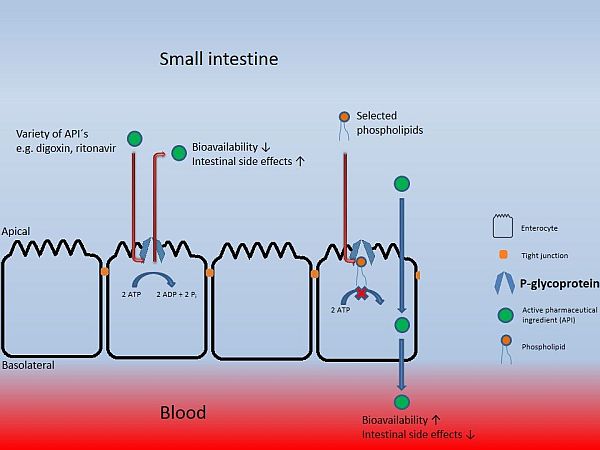
However, membranes of mucosal cells feature various efflux transporters - such as the so-called P-glycoprotein (P-gp) - that are able to actively return many active pharmaceutical ingredients into the intestinal lumen. This process strongly reduces the systemic bioavailability of these agents and thus their therapeutic efficacy.
At this Department, one aspect of the PhD thesis by Dr. Silke Simon is to investigate the inhibition of the efflux transporter, P-gp, by certain phospholipids, as well as to identify the molecular mechanisms underlying this process.
The studies are being conducted in various in vitro cell models: Caco-2 cells originate from a human colon carcinoma, yet have many characteristics of small intestinal epithelial cells, by which they qualify as an excellent tool for bioavailability. Also, direct evidence for P-gp inhibition can be drawn from experiments using mdr1-transfected cell lines or by studying P-gp-ATPase activity. First in-vivo experiments were done in rats together with Professor Dr. Gert Fricker (Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy, University Heidelberg, Germany), showing that phospholipids can markedly improve the oral bioavailability of the P-gp substrate Ritonavir.
Manuel Weinheimer is currently working on this research area in the course of his PhD thesis.
Funding
From 2009 to 2012, this project was financially supported by the Phospholipid Research Center e.V., Heidelberg, Germany.
Simon S, Schubert R: Inhibitory Effect of Phospholipids on P-Glycoprotein: Cellular studies in Caco-2, MDCKII mdr1 and MDCKII wildtype cells and P-gp ATPase activity measurements; Biochim. Biophys. Acta – Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1821, 1211-1123, 2012. [Epub]